中科院报告指美国疫情或始于2019年9月
9/23/2021
中国科学院预印本平台(ChinaXiv)22日发布的一项基于大数据建模分析的疫情起源时间研究结果指出,美国疫情较大概率于2019年9月前后已开始流行。
据中国央视财经报道,研究人员依据传染病传播模型和大数据分析的方法,建立优化模型,基于已公开数据对美国东北部12州和中国武汉市、浙江省等地的疫情起源时间进行了推断。
研究结果显示,对于美国东北部12州,疫情首例感染发生概率50%的日期多数位于2019年8月到10月,最早是罗德岛州的2019年4月26日,最晚是特拉华州的2019年11月30日,均早于美国官方公布的全美首例确诊日期2020年1月20日。计算结果表明,美国疫情较大概率于2019年9月前后已开始流行。
计算显示,中国武汉市首例感染发生概率50%的日期为2019年12月20日,中国浙江省首例感染发生概率50%的日期为2019年12月23日。据此推断,中国疫情较大概率于2019年12月下旬已开始流行。研究认为,这一结论与流行病学调查结果基本相符,证明该计算方法准确可靠。
COVID-19 might have started to spread in September 2019 in the United States: study
Source: Xinhua
9/23/2021

BEIJING, Sept. 23 (Xinhua) — Chinese researchers have discovered by employing big-data analysis that the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States might have started to spread around in September 2019, earlier than the officially announced date of its first confirmed case.
According to a new article published Wednesday as a preprint in ChinaXiv, a series of previous studies showed that the United States, Spain, France, Italy, Brazil and other countries had shown signs of being hit by the virus before its outbreak in China.
ChinaXiv is an online publishing service operated by the National Science Library, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The article, titled “Dating the First Case of COVID-19 Epidemic from a Probabilistic Perspective,” suggested that the qualitative and quantitative analysis of infectious diseases, done by combining mathematical models and artificial-intelligence technology, can reveal the epidemic law of infectious diseases.
The researchers set up an optimized model using the epidemic transmission model and big-data analysis method, and inferred the dates of the first infection cases in 12 northeastern U.S. states and in China’s Wuhan City and Zhejiang Province, based on published data.
The result indicated that, for the 12 U.S. states, the possible dates of the first infection, with a probability of 50 percent, fall mostly between August and October 2019, while the earliest is April 26, 2019 on Rhode Island, and the latest is Nov. 30, 2019 in Delaware.
All of the dates indicated by the data are earlier than Jan. 20, 2020, the officially announced date of the first confirmed case in the United States, showing that the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States started to spread around September 2019 with a high confidence probability.
The result also showed that the date of the first COVID-19 case in Wuhan, with a probability of 50 percent, is Dec. 20, 2019, and the date for Zhejiang is Dec. 23, 2019. It infers that the COVID-19 in China is most likely to have started in late December 2019.
The article said this is consistent with the results of the epidemiological investigation, which proves that the calculation method is accurate and reliable.
冠病在美国夺走的人命已超越1918年流感大流行
文 / 陈慧璋
9/21/2021

(早报讯)根据最新统计,美国因感染冠病而死亡的人数已超过1918年流感大流行在美国造成的死亡人数。
法新社报道,美国约翰斯霍普金斯大学的冠病疫情数据显示,截至9月17日,美国有67万5722起冠病死亡病例。在世界第一次大战的最后一年——1918年暴发的流感大流行在美国夺走了67万5000条人命。
美国疾病控制与预防中心(CDC)此前表示,1918年流感大流行被认为是近代史上最致命的流行病,世界三分之一的人口受感染,并造成至少5000万人死亡。
约翰斯霍普金斯大学的数据还显示,截至目前全球冠病累计死亡病例接近470万起。尽管美国人口只占世界总人口的5%,但病亡人数已超却占了世界病亡人数的14%。
美国疾控中心前主任弗里登9月13日在推特上预言美国冠病死亡人数将超过1918年流感大流行,他说:“很大程度上这个悲剧是可以避免的,但却还在继续发生。我们不能对此无动于衷。”
1918年美国的总人口不到现在的三分之一,这意味着当时流感造成的死亡人数相当于今天的大约220万人。
美国每小时就有约42人死于冠病
文 / 潘万莉
8/18/2021
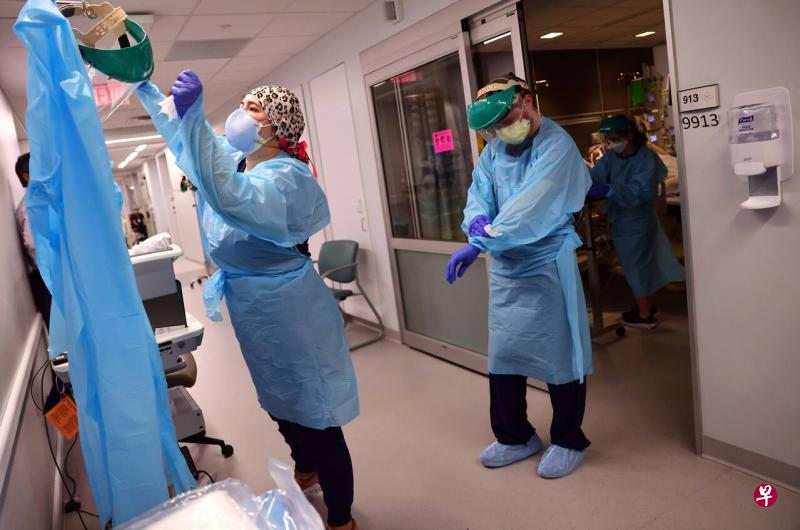
(早报讯)由于德尔塔(Delta)变种病毒持续在美国疫苗接种率较低的地区肆虐,美国周二染疫死亡人数超过1000起,相当于每小时就有约42人死于冠病。
过去一个月来美国染疫死亡人数大幅增加,平均每天多达769人病殁,创下今年4中旬以来新高。
为了防止疫情持续失控,拜登政府周二晚间证实,要求旅客在飞机、火车和巴士,以及在机场和火车站戴口罩的规定将延长至明年1月中旬。
和其他许多国家一样,德尔塔变种病毒令美国面临重大挑战。
根据各州数据的统计结果显示,周二美国多达1017人死于冠病,使去年疫情爆发以来累计死亡人数逼近62.3万人,在全世界排名第一。
上一次美国的单日染疫死亡人数破千人,是发生在今年3月。
近来美国医院涌入大量的新患者,数据显示过去两周染疫住院人数约增加70%。
此外,过去12天,美国平均每日新增确诊数都超过10万起,一直保持在六个月的新高水准。
接种后出现死亡病例 比利时限制强生疫苗的使用年龄
文 / 潘万莉
5/26/2021
(早报讯)比利时一名40岁以下的妇女近日在接种强生冠病疫苗后出现严重的血栓和血小板减少等症状,其在被送往医院后于5月21日不治身亡。比利时卫生部门当地时间5月26日发表声明称,该国将暂停在41岁以下的人群中使用强生冠病疫苗。
声明指出,比利时已要求欧洲药品管理局对该起死亡病例与强生疫苗的关联性进行调查,该国将等待药管局就疫苗安全性问题做出更为详尽的分析之后再决定是否取消使用年龄限制。
欧洲药品管理局曾在4月20日表示,强生疫苗可能与接种者出现血栓有关联,但接种该疫苗的益处大于风险,欧盟成员国可以自行决定如何使用这种疫苗。
美国食药局发文 强生冠病疫苗被迫暂停使用
4/13/2021
(早报讯)美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)13日在推特表示,已和美国疾控中心(CDC)共同发布声明,出于充分谨慎,建议暂停接种美国强生公司生产的冠病疫苗。
FDA在推文中表示,截至4月12日,美国已经有六名强生疫苗接种者出现血栓症状,目前来看这一症状极其罕见。FDA称,对这种血栓症状的治疗可能会不同于常用疗法。CDC将在当地时间14日召开会议,进一步讨论强生疫苗的血栓病例。
据美药管局网站显示,接种强生冠病疫苗后的常见不良反应为注射部位疼痛、头痛、疲劳、肌肉痛和恶心,大多为轻度至中度,持续一两天。
近日,位于美国马里兰州巴尔的摩市的一家冠病疫苗制造工厂的员工误将两种不同疫苗的原料混合,导致1500万剂庄生冠病疫苗被迫销毁,这影响到该疫苗在全美的供应和分发。美国媒体援引联邦政府官员的表态称,本周全美美国强生冠病疫苗的供应量将下降85%。
Joint CDC and FDA Statement on Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine
The following statement is attributed to Dr. Peter Marks, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research and Dr. Anne Schuchat, Principal Deputy Director of the CDC
For Immediate Release: April 13, 2021
Statement From: Director – Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER)
Peter Marks M.D., PhD.
As of April 12, more than 6.8 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson (Janssen) vaccine have been administered in the U.S. CDC and FDA are reviewing data involving six reported U.S. cases of a rare and severe type of blood clot in individuals after receiving the J&J vaccine. In these cases, a type of blood clot called cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) was seen in combination with low levels of blood platelets (thrombocytopenia). All six cases occurred among women between the ages of 18 and 48, and symptoms occurred 6 to 13 days after vaccination. Treatment of this specific type of blood clot is different from the treatment that might typically be administered. Usually, an anticoagulant drug called heparin is used to treat blood clots. In this setting, administration of heparin may be dangerous, and alternative treatments need to be given.
CDC will convene a meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) on Wednesday to further review these cases and assess their potential significance. FDA will review that analysis as it also investigates these cases. Until that process is complete, we are recommending a pause in the use of this vaccine out of an abundance of caution. This is important, in part, to ensure that the health care provider community is aware of the potential for these adverse events and can plan for proper recognition and management due to the unique treatment required with this type of blood clot.
Right now, these adverse events appear to be extremely rare. COVID-19 vaccine safety is a top priority for the federal government, and we take all reports of health problems following COVID-19 vaccination very seriously. People who have received the J&J vaccine who develop severe headache, abdominal pain, leg pain, or shortness of breath within three weeks after vaccination should contact their health care provider. Health care providers are asked to report adverse events to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System at https://vaers.hhs.gov/reportevent.html.
CDC and FDA will provide additional information and answer questions later today at a media briefing. A recording of that media call will be available on the FDA’s YouTube channel.
The FDA, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, protects the public health by assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices. The agency also is responsible for the safety and security of our nation’s food supply, cosmetics, dietary supplements, products that give off electronic radiation, and for regulating tobacco products.
###
Six Spaces Home Staging

Contact: Hongliang Zhang
Tel: 571-474-8885
Email: zhl19740122@gmail.com
WHO recommends follow-up care, low-dose anticoagulants for COVID-19 patients
26 January 2021
WHO recommends that patients who have COVID-19 – both confirmed and suspected – should have access to follow-up care if they have persistent, new or changing symptoms.
This is one of the recommendations made by WHO in revised clinical management guidelines.
Evidence was gathered on the post COVID condition, so-called ‘long COVID’, where people who have recovered from COVID-19 continue to have longer-term issues like extreme fatigue, persistent cough and exercise intolerance.
Understanding this condition is one of WHO’s priority areas of work. In February 2021, WHO will organize a series of consultations to reach consensus on a description of this condition and its subtypes, and case definitions. This scientific understanding will inform the name of the condition. The consultations will include a broad range of stakeholders, including patient groups.
For COVID-19 patients at home, WHO suggests the use of pulse oximetry to measure oxygen levels in the blood. This needs to be coordinated with other aspects of home care, such as education for the patient and care provider and regular follow-up of the patient.
For hospitalized patients, WHO suggests the use of low dose anticoagulants for preventing the blood clots forming in blood vessels (thrombosis).
For hospitalized patients who are taking supplemental oxygen (including high-flow nasal oxygen) or non-invasive ventilation, WHO suggests positioning patients on their stomachs to increase oxygen flow (awake prone positioning).
The guidelines also include recommendations on the use of care bundles to systematize care provision for COVID-19 patients, as well as a recommendation to favour clinical judgement over models in making decisions for the patient’s care.
The recommendations were made by an independent panel of experts, the Guideline Development Group, on the basis of detailed rapid reviews of all available evidence.
The guidelines are a living document, updated regularly as more data becomes available.
世卫不建议接种莫德纳疫苗:应防止接种者出现过敏性休克
来源:海外网
2021年01月27日
海外网1月26日电 世界卫生组织专家组对莫德纳新冠疫苗mRNA-1273的数据进行评估后,26日发布了该疫苗的暂行使用建议;世卫组织将于2月底就是否将该疫苗纳入紧急使用清单作出决定。
据俄罗斯卫星通讯社26日消息,世卫组织免疫战略咨询专家组1月21日开会评估了莫德纳新冠疫苗mRNA-1273Ⅲ期临床试验的初步数据。考虑到接种这款疫苗后可能出现过敏反应,世卫组织专家建议只在能防止接种者出现过敏性休克的条件下提供接种。专家组不建议孕期妇女接种mRNA-1273,除非她们属于高风险人群(比如医疗工作者)。专家组指出,鉴于目前疫苗不足,加上没有证据表明疫苗能降低新冠病毒传播风险,不建议为旅行者优先接种。
据新华社早前报道,美国疾病控制和预防中心22日发布的一份报告显示,截至1月10日,全美共有4041396人接种了第一剂美国莫德纳公司研发的新冠疫苗,共报告了1266起不良反应事件,其中包括10起过敏反应。美疾控中心介绍,过敏反应是危及生命的严重不良反应,通常在接种疫苗后几分钟至几小时内发生。这10起被确认为过敏反应,其中9起发生在接种后15分钟之内,1起发生在接种后45分钟;108起可能为包括过敏反应在内的严重不良反应事件,需要进一步核查。
美国食品和药物管理局于2020年12月18日批准了莫德纳新冠疫苗的紧急使用授权申请。这是继美国辉瑞制药有限公司与德国生物新技术公司联合研发的新冠疫苗之后第二款获批在美紧急使用的新冠疫苗,被允许用于18岁及以上人群,共接种两剂,间隔1个月。(海外网 侯兴川)



