抢普亭人才 美拟为俄顶尖科学家放宽签证规定
中央社 | 华盛顿
5/01/2022

熟知内情人士透露,拜登总统政府计划对受过高等教育且有意赴美的俄国人民免除某些签证规定,以抢夺俄国最优秀的创新人才。
彭博(Bloomberg)报导,白宫最近向国会提交补充预算请求,其中包括一项提案,就是取消俄罗斯专业人士申请赴美工作签证时必须已有雇主的规定。
提案称,这将适用于在美国或其他国家获得科学、技术、工程、数学等学科硕士或博士学位的俄罗斯公民。
白宫国家安全会议发言人证实,此举意在于短期削弱俄国总统普亭的高科技资源,在长期动摇俄国的创新基础,同时也有利于美国经济和国家安全。
明确地说,拜登政府希望在半导体、太空科技、网络安全、先进制造、先进运算、核子工程、人工智能、飞弹推进技术和其他专业科学领域拥有丰富经验的顶级俄罗斯人能比较容易移居美国。
拜登政府官员表示,他们发现有相当多高技能科技工作人员逃离俄罗斯,因为普亭入侵乌克兰招致美国与盟国实施制裁,使得留在俄国工作的金钱收益有限。
这项条款将在4年后到期,至于「移民与国籍法」(Immigration and Nationality Act)中的审查程序、费用或其他规定则维持不变。

2月24日俄军入侵乌克兰后,俄罗斯专业人士便开始外逃。芝加哥大学经济学家索宁(Konstantin Sonin)3月7日在推特上写道:「在过去10天,有超过20万人逃离俄罗斯,这是百年未见的悲剧性出走潮。」
国际传真社(Interfax)引据俄罗斯电子通信协会(Russian Association for Electronic Communications)的估计报导,4月份可能有7万至10万名通信科技专业人才试图移民海外。
美国与七大工业国集团(G7)的一些盟国最近几周也针对给予俄罗斯科学家受保护地位进行了讨论,包括那些在欧洲核子研究组织(CERN)工作的俄国人。
拥有最大粒子物理实验室的CERN在乌克兰战事爆发后,已暂停与俄罗斯的大部分合作。

工作移民绿卡 6.65万名额作废 14.1万亲属移民名额转入
世界新闻网
4/16/2022

受到川普执政时期移民规定趋严影响,加上疫情期间人手短缺导致作业耽搁,2021会计年度约有6万6500个工作移民(employment-based,EB)绿卡名额并未使用。
国务院本周公布数据显示,2021会计年度约有26万2000个工作移民绿卡名额可用,但受疫情期间各种防疫规定限制,加上人手不足,使得美国驻外大使馆及领事馆处理绿卡申请时遭遇挑战。
美国公民暨移民服务局(U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services,USCIS)发言人说,工作移民绿卡申请案是移民局优先处理的工作项目。
Healthcare Certification and ESL Programs
统计数据显示,2021会计年度亲属移民(family-based,FB)绿卡名额共计有22万6000个,其中有14万1000个名额并未使用。
根据规定,工作移民绿卡名额若未使用便将失效作废,但未获使用的亲属移民绿卡名额则可纳入下一个会计年度工作移民绿卡名额。2022会计年度将于9月30日截止。
国务院指出,2022会计年度工作移民绿卡名额共计约有28万个。外籍人士拿到绿卡后,便取得在美生活及工作的永久居留权。原本持有客工签证(guest worker visas)的外籍人士拿到绿卡后,则可更换雇主。绝大多数工作移民绿卡申请是由国土安全部旗下的公民暨移民服务局审理,亲属移民绿卡申请主要则由国务院处理。

过去几个月间,国会议员曾尝试推动法案,让前一个会计年度没有使用的绿卡名额,可以留待下一个会计年度使用,但最后立法便未成功。众院司法委员会推动的众院第3648号草案(H.R. 3648)近来颇有进展,提案内容为取消各个国家工作移民绿卡名额上限,因为这项措施导致某些国家的绿卡申请案出现塞车。提案内容也同意为绿卡申请案遭到延误的申请人放宽旅行限制,并对于更换工作提供更多弹性空间。
公民暨移民局为了加快工作移民绿卡申请案的审理脚步,已根据不同地区办公室、服务中心的工作量展开资源调度,并且尽可能重复使用生物识别资讯(biometric information),同时依照风险评估结果为某些申请人取消面试要求。
统计显示,2021年1月间,移民局未拆封的签证申请案约有100万件,但到同年7月已在处理。
USCIS Announces New Actions to Reduce Backlogs, Expand Premium Processing, and Provide Relief to Work Permit Holders
Release Date: 03/29/2022
WASHINGTON— Today, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services is announcing a trio of efforts to increase efficiency and reduce burdens to the overall legal immigration system. USCIS will set new agency-wide backlog reduction goals, expand premium processing to additional form types, and work to improve timely access to employment authorization documents. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic and resource constraints resulting from the prior administration, USCIS inherited a significant number of pending cases and increased processing times. Through today’s actions by the Biden administration, USCIS is acting to reduce these caseloads and processing times, while also ensuring that fair and efficient services are available to applicants and petitioners.
“USCIS remains committed to delivering timely and fair decisions to all we serve,” said USCIS Director Ur M. Jaddou. “Every application we adjudicate represents the hopes and dreams of immigrants and their families, as well as their critical immediate needs such as financial stability and humanitarian protection.”
Reducing Processing Backlogs
To reduce the agency’s pending caseload, USCIS is establishing new internal cycle time goals this month. These goals are internal metrics that guide the backlog reduction efforts of the USCIS workforce and affect how long it takes the agency to process cases. As cycle times improve, processing times will follow, and applicants and petitioners will receive decisions on their cases more quickly. USCIS will increase capacity, improve technology, and expand staffing to achieve these new goals by the end of FY 2023.

The agency’s publicly posted processing times show the average amount of time it took USCIS to process a particular form – from when the agency received the application until a decision was made on the case. Internally, USCIS monitors the number of pending cases in the agency’s workload through a metric called “cycle times.” A cycle time measures how many months’ worth of pending cases for a particular form are awaiting a decision. As an internal management metric, cycle times are generally comparable to the agency’s publicly posted median processing times. Cycle times are what the operational divisions of USCIS use to gauge how much progress the agency is, or is not, making on reducing our backlog and overall case processing times.
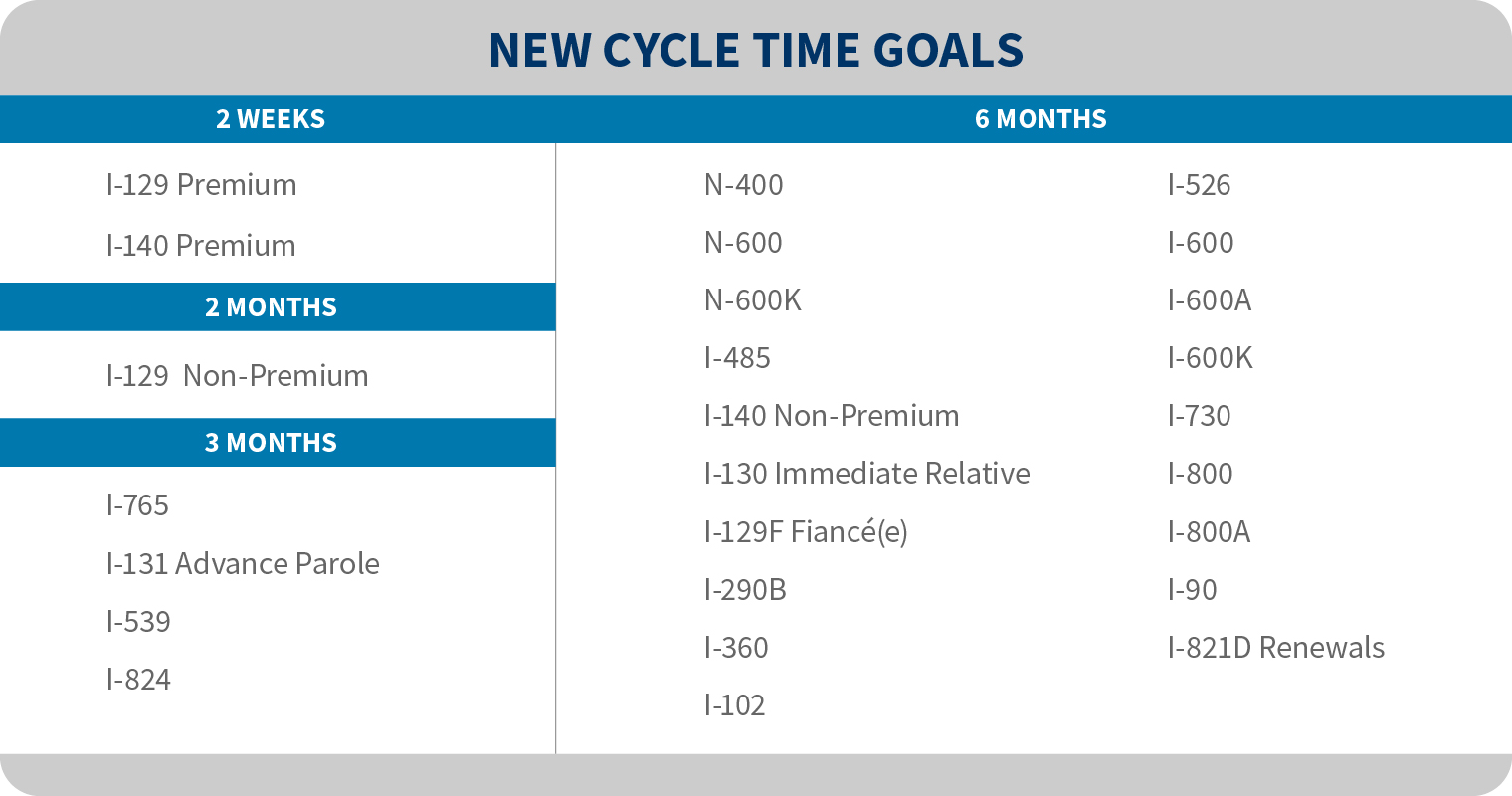

Expanding Premium Processing
Today the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) announced a final rule that aligns premium processing regulations with the Emergency Stopgap USCIS Stabilization Act. The rule codifies premium processing fees and adjudication timeframes provided by Congress.
Premium processing is an expedited adjudication service now available only to petitioners filing a Form I-129, Petition for a Nonimmigrant Worker, and to certain employment-based immigrant visa petitioners filing a Form I-140, Immigrant Petition for Alien Workers. This final rule expands the categories of forms ultimately eligible for premium processing services, including Form I-539, Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status; Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization; and additional classifications under Form I-140.
USCIS intends to begin implementing, through a phased approach, premium processing availability of Form I-539, Form I-765 and Form I-140 in fiscal year 2022. USCIS will also adhere to the congressional requirement that the expansion of premium processing must not cause an increase in processing times for regular immigration benefit requests.

USCIS plans to begin this phased implementation process by expanding premium processing eligibility to Form I-140 filers requesting EB-1 immigrant classification as a multinational executive or manager, or EB-2 immigrant classification as a member of professions with advanced degrees or exceptional ability seeking a national interest waiver.
Improving Access to Employment Authorization Documents
USCIS continues to make progress toward a temporary final rule currently named “Temporary Increase of the Automatic Extension Period of Employment Authorization and Documentation for Certain Renewal Applicants.”
In recent months, USCIS has begin streamlining many EAD processes, including extending validity periods for certain EADs and providing expedited work authorization renewals for healthcare and childcare workers. The temporary final rule aims to build on this progress and to ensure certain individuals will not lose their work authorization status while their applications are pending.
A full list of prior actions USCIS has taken to reduce processing times and the agency’s pending caseload is available on our website.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 03/29/2022
FY 2023 H-1B Cap Initial Registration Period Opens on March 1
Release Date: 01/28/2022
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services today announced that the initial registration period for the fiscal year 2023 H-1B cap will open at noon Eastern on March 1 and run through noon Eastern on March 18, 2022. During this period, prospective petitioners and representatives will be able to complete and submit their registrations using our online H-1B registration system.
USCIS will assign a confirmation number to each registration submitted for the FY 2023 H-1B cap. This number is used solely to track registrations; you cannot use this number to track your case status in Case Status Online.
Prospective H-1B cap-subject petitioners or their representatives are required to use a myUSCIS online account to register each beneficiary electronically for the selection process and pay the associated $10 H-1B registration fee for each registration submitted on behalf of each beneficiary. Prospective petitioners submitting their own registrations (U.S. employers and U.S. agents, collectively known as “registrants”) will use a “registrant” account. Registrants will be able to create new accounts beginning at noon Eastern on Feb. 21.
Representatives may add clients to their accounts at any time, but both representatives and registrants must wait until March 1 to enter beneficiary information and submit the registration with the $10 fee. Prospective petitioners or their representatives will be able to submit registrations for multiple beneficiaries in a single online session. Through the account, they will be able to prepare, edit, and store draft registrations prior to final payment and submission of each registration.
If we receive enough registrations by March 18, we will randomly select registrations and send selection notifications via users’ myUSCIS online accounts. We intend to notify account holders by March 31.
An H-1B cap-subject petition, including a petition for a beneficiary who is eligible for the advanced degree exemption, may only be filed by a petitioner whose registration for the beneficiary named in the H-1B petition was selected in the H-1B registration process.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 01/28/2022
How to Make an Expedite Request
ALERT: If you are a healthcare worker
ALERT: If you are a healthcare worker
If you are a healthcare worker
- Who has a pending Employment Authorization Document (EAD) renewal application (Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization); and
- Whose EAD expires within 30 days or less, or has already expired:
Call the USCIS Contact Center at 800-375-5283 (TTY 800-767-1833) to request expedited processing of your EAD based on your circumstance as a healthcare worker with an EAD that will expire within 30 days or has already expired. To determine whether you are a qualifying healthcare worker, see this DHS advisory memorandum (“Healthcare / Public Health” section, pages 7-9) (PDF). Be prepared to provide evidence of your profession or current employment as a healthcare worker. If the evidence you provide is not sufficient, we may not accommodate your request for expedited processing of your Form I-765. Expedited processing means only that USCIS will process the application faster.
In General
You may ask USCIS to expedite adjudication of a benefit request (such as an application or petition) for an immigration benefit.
USCIS:
- Considers all expedite requests on a case-by-case basis;
- May require additional documentation to support a request; and
- Has the sole discretion to decide whether to accommodate a request.
Because granting an expedite request means that USCIS would adjudicate the requestor’s benefit ahead of others who filed earlier, we carefully weigh the urgency and merit of each expedite request. We may consider an expedite request if it meets one or more of the following criteria or circumstances:
- Severe financial loss to a company or person, provided that the need for urgent action is not the result of the petitioner’s or applicant’s failure to:
- Timely file the benefit request, or
- Timely respond to any requests for additional evidence;
A company can demonstrate that it would suffer a severe financial loss if it is at risk of failing, losing a critical contract, or having to lay off other employees. For example, a medical office may suffer severe financial loss if a gap in a doctor’s employment authorization would require the medical practice to lay off its medical assistants.
Job loss may be sufficient to establish severe financial loss for a person, depending on the individual circumstances. For example, the inability to travel for work that would result in job loss might warrant expedited treatment. The need to obtain employment authorization by itself, without evidence of other compelling factors, does not warrant expedited treatment. In addition, severe financial loss may also be established where failure to expedite would result in a loss of critical public benefits or services.
- Emergencies and urgent humanitarian reasons;
In the context of an expedite request, humanitarian reasons are those related to human welfare. Examples may include, but are not limited to, illness, disability, extreme living conditions, death in the family, or a critical need to travel to obtain medical treatment in a limited amount of time. An emergency may include an urgent need to expedite employment authorization for healthcare workers during a national emergency such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, an expedite request may be considered under this criterion in instances where a vulnerable person’s safety may be compromised due to a breach of confidentiality if there is a delay in processing the benefit application. A benefit requestor’s desire to travel for vacation does not, in general, meet the definition of an emergency.
- Nonprofit organization (as designated by the Internal Revenue Service) whose request is in furtherance of the cultural or social interests of the United States;
A nonprofit organization seeking to expedite a beneficiary’s benefit request must demonstrate an urgent need to expedite the case based on the beneficiary’s specific role within the nonprofit in furthering cultural or social interests (as opposed to the organization’s role in furthering social or cultural interests). Examples may include a medical professional urgently needed for medical research related to a specific social U.S. interest (such as the COVID-19 pandemic or other socially impactful research or project) or a university professor urgently needed to participate in a specific and imminent cultural program. Another example is a religious organization that urgently needs a beneficiary’s specific services and skill set to continue a vital social outreach program. In such instances, the religious organization must articulate why the respective beneficiary is specifically needed, as opposed to pointing to a general shortage alone.
- U.S. government interests (such cases identified as urgent by federal agencies such as the U.S. Department of Defense, U.S. Department of Labor, National Labor Relations Board, Equal Opportunity Commission, U.S. Department of Justice, U.S. Department of State, U.S. Department of Homeland Security, or other public safety or national security interests); or
U.S. government interests may include, but are not limited to, cases identified as urgent by other government agencies, including labor and employment agencies, and public safety or national security interests.
For expedite requests made by a federal agency, involving other public safety or national security interests, the national interest need must be immediate and substantive. If the need for the action is not immediate, expedited processing is not warranted. A substantive need does not mean that a delay would pose existential or irreversible consequences to the national interests but rather that the case at hand is of a scale or a uniqueness that requires immediate action to prevent real and serious harm to U.S. interests.
Expedite requests from government agencies (federal, state, or local) must be made by a senior-level official of that agency. If the request relates to employment authorization, the request must demonstrate that the need for a person to be employment-authorized is mission-critical and goes beyond a general need to retain a particular worker or person. Examples include, but are not limited to, a noncitizen victim or witness cooperating with a federal, state, or local agency who is in need of employment authorization because the respective agency is seeking back pay or reinstatement in court proceedings.
- Clear USCIS error.
Not every circumstance that fits in one of these categories will result in expedited processing.
For more information, see USCIS Policy Manual, Volume 1, Part A, Public Services, Chapter 5, Requests to Expedite Applications or Petitions [1 USCIS-PM A.5].
You can generally request expedited processing by calling the USCIS Contact Center at 800-375-5283 (TTY 800-767-1833) or by asking Emma after you have obtained a receipt notice. (You can access Emma by clicking on the Ask Emma icon on the top right of this page). The USCIS Contact Center will not be able to refer the expedite request to the appropriate office without a receipt number.
When you call to request expedited processing, the USCIS Contact Center creates and forwards a service request to the office with jurisdiction over your application or petition. After receiving the service request, the reviewing office may request additional documentation to support expedited processing. A decision on an expedite request is not an approval or a denial of the underlying benefit request. The expedite decision simply informs the requestor whether USCIS will take the benefit request out of date order and issue a decision (approval or denial) faster than the normal processing time.
In accordance with the criteria above, note specific handling procedures in the following circumstances:
Adoptions
See the USCIS Adoption Contact Information webpage for information on how to make expedite requests for adoption cases.
Appeals
Requests for expedited processing of appeals may be included with the appeal. Expedite requests included with the appeal will be reviewed by the office that issued the decision.
For appeals filed with the Administrative Appeals Office (AAO), any expedite request made after the appeal submission should be mailed or faxed directly to AAO. See AAO’s Processing Requests and Contacting the AAO pages for more information.
Regardless of whether the expedite request is submitted with the appeal or afterward, the expedite request should include:
- A cover letter clearly marked “EXPEDITE REQUEST”; and
- Documentary evidence supporting the request for expedited processing of the appeal.
Requests for expedited processing of appeals filed with the Board of Immigration Appeals (BIA) should follow the BIA expeditious handling procedures.
Applications for Asylum
Requests for expedited processing on asylum applications should be directed to the office with jurisdiction over the asylum application. See the Affirmative Asylum Interview Scheduling page for more information.
Benefit Requests Pending Outside the United States
Send requests for expedited processing of applications for refugee status to the Resettlement Support Center handling the case abroad. For more information, see the USCIS Questions and Answers: Refugees page.
Send requests for expedited processing of humanitarian parole for beneficiaries located outside of the United States to the Humanitarian Affairs Branch. For more information, see the Humanitarian or Significant Public Benefit Parole for Individuals Outside the United States page.
For all other immigration benefit requests pending with USCIS offices located outside the United States, you may request expedited processing by submitting a written request, along with any supporting documentation, directly to the USCIS office with the benefit request.
For contact information for USCIS offices located outside the United States, see the USCIS International Immigration Offices page. Requests for expedited processing on matters pending with Department of State (DOS) should follow DOS expeditious handling procedures.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 01/25/2022
USCIS Provides Clarifying Guidance for O-1 Petitions with a Focus on STEM Fields
Release Date 01/21/2022
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services today issued policy guidance clarifying how it evaluates evidence to determine eligibility for O-1A nonimmigrants of extraordinary ability, with a focus on petitions filed for individuals in science, technology, engineering, or math (STEM) fields, as well as how USCIS determines whether an O-1 beneficiary’s prospective work is within their area of extraordinary ability or achievement.
Individuals of extraordinary ability in the sciences, education, business, or athletics may be eligible for O-1A classification. The new update provides examples of evidence that may satisfy the O-1A evidentiary criteria and discusses considerations that are relevant to evaluating such evidence, with a focus on the highly technical nature of STEM fields and the complexity of the evidence often submitted.
The update also emphasizes that, if a petitioner demonstrates that a particular criterion does not readily apply to their occupation, they may submit evidence that is of comparable significance to that criterion to establish sustained acclaim and recognition, and it provides examples of possible comparable evidence that may be submitted in support of petitions for beneficiaries working in STEM fields.
In addition, the update explains that when evaluating whether an individual of extraordinary ability is coming to work in their “area of extraordinary ability,” officers will focus on whether the prospective work involves skillsets, knowledge, or expertise shared with the occupation(s) in which the individual garnered acclaim.
Visit the Policy Manual for Comment page to comment on this update. For more information, see the policy manual update (PDF, 363.79 KB).
Last Reviewed/Updated: 01/21/2022
USCIS Updates Guidance on National Interest Waivers
Release Date 01/21/2022
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services today announced updated guidance on adjudicating requests for “National Interest Waivers” regarding job offer and labor certification requirements for certain advanced degree professionals and individuals of exceptional ability. This includes discussing the unique considerations for persons with advanced degrees in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) fields and entrepreneurs.
Consistent with this Administration’s goal of removing barriers to legal immigration under President Biden’s Executive Order 14012, Restoring Faith in Our Legal Immigration Systems and Strengthening Integration and Inclusion Efforts for New Americans, USCIS is clarifying how the national interest waiver can be used by STEM graduates and entrepreneurs, as well as the significance of letters from governmental and quasi-governmental entities. The updated guidance also serves to promote effective and efficient processing of benefits consistent with the executive order.
An employer seeking to hire a noncitizen must generally obtain a permanent labor certification from the Department of Labor that proves there are no qualified U.S. workers for the position they are seeking and that their employment will not adversely affect similarly employed U.S. workers. The noncitizen may, however, seek a waiver of a job offer, and of the labor certification, if it is in the interest of the United States.
Individuals seeking a national interest waiver must show evidence of an advanced degree or exceptional ability and must also meet three factors that USCIS uses to determine, in its discretion, whether it is in the national interest that USCIS waive the requirement of a job offer, and thus the labor certification. The three factors USCIS considers for a national interest waiver are whether:
- The person’s proposed endeavor has both substantial merit and national importance;
- The person is well positioned to advance the proposed endeavor; and
- It would be beneficial to the United States to waive the job offer and thus the permanent labor certification requirements.
Those seeking a national interest waiver may self-petition using Form I-140, Immigrant Petition for Alien Worker.
This guidance, contained in Volume 6 of the Policy Manual, is effective immediately. The guidance contained in the Policy Manual is controlling and supersedes any related prior guidance.
Visit the Policy Manual for Comment page to comment on this update.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 01/21/2022
USCIS Conducts Third Random Selection from Previously Submitted FY 2022 H-1B Cap Registrations
Release Date 11/19/2021
We recently determined that we needed to select additional registrations to reach the fiscal year (FY) 2022 H-1B numerical allocations, including the advanced degree exemption. On Nov. 19, we selected from among previously submitted electronic registrations using a random selection process. The petition filing period based on registrations selected on Nov. 19 will begin on Nov. 22, 2021, and close on Feb. 23, 2022. Individuals with selected registrations will have their myUSCIS accounts updated to include a selection notice, which includes details about when and where to file.
In July 2021, we conducted a second random selection from among properly submitted electronic registrations for the FY 2022 H-1B numerical allocations. The petition filing period based on registrations selected in July ended on Nov. 3, 2021.
We conducted an initial selection in March 2021. The initial filing period for those with selected registrations for FY 2022 was from April 1, 2021, through June 30, 2021. Per regulation, we take into account historical data related to approvals, denials, revocations, and other relevant factors to calculate the number of registrations needed to meet the H-1B numerical allocations for a given fiscal year. Only those petitioners with selected registrations for FY 2022 are eligible to file H-1B cap-subject petitions.
An H-1B cap-subject petition must be properly filed at the correct service center and within the filing period indicated on the relevant registration selection notice. Online filing is not available for H-1B petitions. Petitioners filing H-1B petitions must do so by paper and must include a printed copy of the applicable registration selection notice with the FY 2022 H-1B cap-subject petition.
Registration selection only indicates that petitioners are eligible to file H-1B cap-subject petitions; it does not indicate that the petition will be approved. Petitioners filing H-1B cap-subject petitions, including those petitions eligible for the advanced degree exemption, must still submit evidence and establish eligibility for petition approval based on existing statutory and regulatory requirements.
For more information, visit the H-1B Cap Season page.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 11/19/2021
Employment authorization implemented for Hong Kong residents covered under Deferred Enforced Departure
By Berry Appleman & Leiden LLP
10/20/2021
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) provided information today on how Hong Kong residents covered by Deferred Enforced Departure (DED) apply for employment authorization.
Key Points:
- DED and employment authorization for noncitizens covered by DED for Hong Kong is effective from Aug. 5, 2021, through Feb. 5, 2023, except for noncitizens who:
- Have voluntarily returned to Hong Kong or the People’s Republic of China (PRC) after Aug. 5, 2021.
- Have not continuously lived in the U.S. since Aug. 5, 2021.
- Are inadmissible under the Immigration and Nationality Act.
- Have been convicted of any felony or two or more misdemeanors in the U.S.
- Are subject to extradition.
- Are considered a present danger to public safety or have potentially serious adverse foreign policy consequences for the U.S. if they remain in the country.
- USCIS said Wednesday that Hong Kong residents can apply for an Employment Authorization Document by submitting a completed Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization.
- Individuals can apply for travel authorization by submitting, Form I-131, Application for Travel Document.
Additional Information: Eligibility requirements for Hong Kong residents who are covered by DED are based on the terms described in the President Joe Biden’s directive and any relevant requirements established by the Department of Homeland Security. The full USCIS announcement can be found here.
USCIS Implements Employment Authorization for Individuals Covered by Deferred Enforced Departure for Hong Kong Residents
Release Date: 10/20/2021
Eligible Hong Kong Residents May Apply for EADs and Travel Authorization
WASHINGTON — U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) today issued a Federal Register notice with information on how to apply for employment authorization for eligible Hong Kong residents covered under the president’s Aug. 5 memorandum directing Deferred Enforced Departure (DED) for 18 months, through Feb. 5, 2023.
DED for Hong Kong residents applies only to certain eligible Hong Kong residents who were present in the United States as of Aug. 5, 2021; who have continuously resided here since that date; and who meet other eligibility criteria described in the president’s memorandum. For purposes of this DED policy, Hong Kong residents are individuals of any nationality, or without nationality, who have met the requirements and been issued a Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) passport, a British National Overseas passport, a British Overseas Citizen passport, a Hong Kong Permanent Identity Card, or an HKSAR Document of Identity for Visa Purposes.
There is no application for DED. Eligibility requirements for Hong Kong residents who are covered under DED are based on the terms described in the president’s directive and any relevant implementing requirements established by the Department of Homeland Security.
Eligible Hong Kong residents may apply for an Employment Authorization Document by submitting a completed Form I-765, Application for Employment Authorization. Eligible Hong Kong residents covered by the president’s DED memorandum may also receive travel authorization. Individuals must file Form I-131, Application for Travel Document, for advance parole if they wish to travel based on DED.
For more information on USCIS and its programs, please visit uscis.gov or follow us on Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, Facebook and LinkedIn.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 10/20/2021

USCIS Extends Flexibility for Responding to Agency Requests
Release Date: 09/24/2021
In response to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services is extending the flexibilities it announced on March 30, 2020, to assist applicants, petitioners and requestors who are responding to certain:
- Requests for Evidence;
- Continuations to Request Evidence (N-14);
- Notices of Intent to Deny;
- Notices of Intent to Revoke;
- Notices of Intent to Rescind;
- Notices of Intent to Terminate regional centers; and
- Motions to Reopen an N-400 Pursuant to 8 CFR 335.5, Receipt of Derogatory Information After Grant.
In addition, USCIS will consider a Form I-290B, Notice of Appeal or Motion, or Form N-336, Request for a Hearing on a Decision in Naturalization Proceedings (Under Section 336 of the INA), if:
- The form was filed up to 60 calendar days from the issuance of a decision we made; and
- We made that decision anytime from March 1, 2020, through Jan. 15, 2022
Notice/Request/Decision Issuance Date:
This flexibility applies to the above documents if the issuance date listed on the request, notice or decision is between March 1, 2020, and Jan. 15, 2022, inclusive.
Response Due Date:
USCIS will consider a response to the above requests and notices received within 60 calendar days after the response due date set in the request or notice before taking any action. Additionally, we will consider a Form N-336 or Form I-290B received up to 60 calendar days from the date of the decision before we take any action.
Please visit uscis.gov/coronavirus for USCIS updates.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 09/24/2021
USCIS Extends Evidence of Status for Conditional Permanent Residents to 24 Months with Pending Form I-751 or Form I-829
Release Date: 09/03/2021
Starting Sept. 4, 2021, USCIS is extending the time that receipt notices can be used to show evidence of status from 18 months to 24 months for petitioners who properly file Form I-751, Petition to Remove Conditions on Residence, or Form I-829, Petition by Investor to Remove Conditions on Permanent Resident Status. We are making the change from 18 to 24 months to accommodate current processing times for Form I-751 and Form I-829, which have increased over the past year.
Conditional permanent residents who properly file Form I-751 or Form I-829 will receive a receipt notice that can be presented with their Form I-551, Permanent Resident Card (also known as a Green Card), as evidence of continued status for up to 24 months past the expiration date on their Green Card, while their case remains pending with USCIS.
Additionally, we will issue new receipt notices to eligible conditional permanent residents who properly filed their Form I-751 or Form I-829 before Sept. 4 and whose cases are still pending. Those receipt notices will also serve as evidence of continued status for 24 months past the expiration date on their Green Card.
As a reminder, conditional permanent residents who plan to be outside of the United States for a year or more should apply for a reentry permit by filing Form I-131, Application for Travel Document, before leaving the country. For more information on International Travel as a Permanent Resident, see our Green Card page.
Last Reviewed/Updated: 09/03/2021






